How to leave Maine residency?

Leaving Maine residency can help you reduce taxes and improve your financial situation, especially if you’re moving for better job opportunities, retirement, or a different lifestyle. Maine has an income tax rate that can reach up to 7.15%, and if you’re a resident, you’re taxed on your worldwide income. For many people, especially digital nomads, retirees, or expats, moving to a state with no or lower taxes can make a big difference.
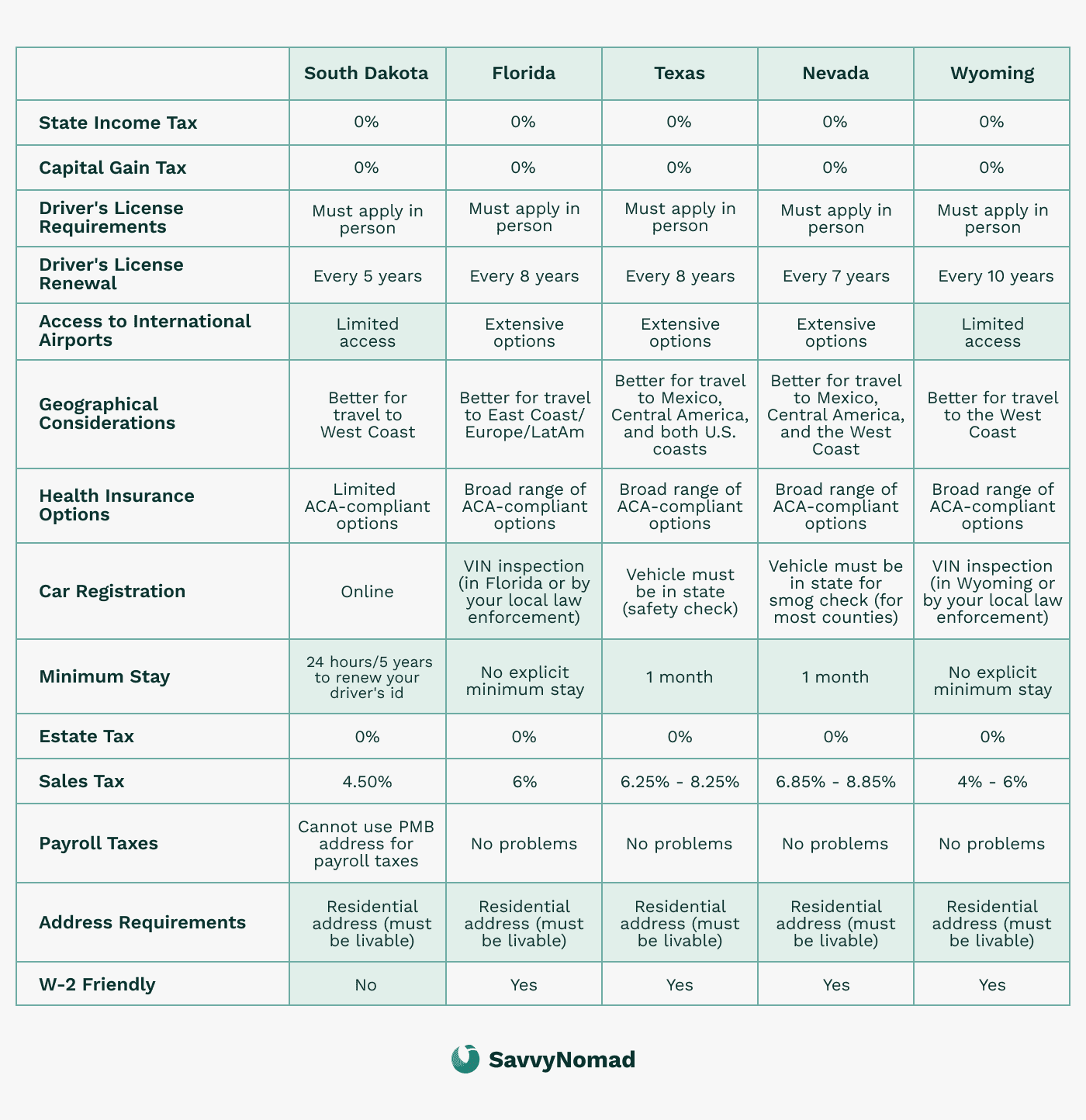
Some people leave Maine for warmer weather, lower living costs, or to be closer to family. States like Florida, Texas, and Nevada are popular choices because they don’t have state income tax. Whether you’re looking to save money or simply want a change, this guide will walk you through the steps to leave Maine residency, establish a new home in another state, and manage any ongoing tax responsibilities.
By following these steps carefully, you can enjoy the benefits of your new state while reducing the risk that Maine still treats you as a resident for tax purposes.
Steps to leaving Maine residency
Step 1: Establish a new domicile
The first step in leaving Maine residency is to set up your new permanent home in another state. This means not only physically moving but also proving that your new state is now your primary residence.
1) Establish new residency
- Secure a residential address: If you buy a home, you may want to look into available credits, like Florida’s homestead exemption.
- File a Declaration of Domicile: In states like Florida, you can file a legal document stating that your new state is now your permanent home, making it official.
This can be especially useful for digital nomads and expats who want a Florida documentation footprint in a tax friendly state, while recognizing that the address itself does not guarantee any particular tax outcome or acceptance by every agency or institution.
Residency guides:
2) Relocate your belongings
Move your personal belongings to your new state to show that you are serious about making it your primary home. This includes household items, vehicles, and anything else that shows you intend to live in your new state permanently.
3) Spend time in your new state
The more time you spend in your new state, the better. It proves that you are truly living there and not just visiting. Avoid spending too much time in Maine, as it could lead to confusion about your residency status.
4) Transfer IDs and vehicle registrations
Update your driver’s license and vehicle registration to your new state. This is a clear and simple way to show that your new state is now your legal home.
5) Register to vote (if eligible)
Register to vote in your new state as soon as possible if you are eligible. Voting is an important way to show your commitment to being part of your new community and is a strong supporting indicator of residency, but it is considered together with many other facts and does not by itself determine your tax status.
6) Update financial accounts
Change your address with banks, credit card companies, and other financial institutions. This helps keep all your accounts consistent with your new state of residency.
7) Notify your employer
Let your employer know about your move and make sure your payroll and tax withholdings are updated to your new state. This helps prevent Maine state income tax from continuing to be withheld after you move, although your actual Maine tax liability will still depend on your own filings and Maine’s rules.
By following these steps, you’ll create a strong foundation for proving your new residency and reducing the risk of being taxed by Maine after your move.

Step 2: Sever ties with Maine
Once you have established a new domicile, the next important step is to cut all significant ties with Maine. This helps reduce the risk that Maine tax authorities continue to treat you as a resident for tax purposes.
Here’s how to do it:
1) Close Maine financial ties
- Close local bank accounts: If you have any bank accounts in Maine, it’s a good idea to close them and move your funds to banks in your new state. This shows that your financial activities are no longer based in Maine.
- Update personal records: Update your address with the IRS, Social Security, and any other relevant entities. Keeping all personal and financial records in your new state helps solidify your move.
2) Sell or lease property
If you own property in Maine, selling or leasing it out can show that you no longer plan to live there. If you choose to lease it, make sure it’s on a long-term basis to further separate yourself from the property.
3) Cancel local subscriptions/services
Make sure to cancel any services or subscriptions tied to Maine, such as gym memberships, utilities, or local clubs. Keeping these services active might imply that you still maintain ties to the state.
4) Transfer healthcare and insurance
Set up healthcare in your new state and ensure your health insurance is updated with your new address. This is another way to demonstrate that you have moved your life elsewhere.

Step 3: Time spent outside Maine
To successfully leave Maine residency, it is important to limit the amount of time you spend in the state and to end your Maine domicile. Maine can treat you as a resident if Maine remains your domicile, or under a statutory residency test that looks at your days in the state together with whether you maintain a home there.
Here’s how to manage your time to avoid being classified as a Maine resident:
183-day rule
- Stay well under 183 days: If you spend 183 days or more in Maine in a given year, especially while maintaining a home or other significant ties in the state, Maine may treat you as a resident for tax purposes. To strengthen your nonresident position after you move, you should aim to spend clearly fewer than 183 days in Maine each year and make sure your main home and ties are in your new state.
- Maintain travel records: It’s important to keep records of your time spent outside Maine, such as flight tickets, hotel receipts, and other documentation. This will help you prove, if necessary, that you were not physically present in Maine for 183 days or more.
Maine’s safe harbor rule
Maine has special safe harbor rules for people who are domiciled in Maine but spend most of their time outside the state. Under the general safe harbor, a person who is domiciled in Maine can be treated as a nonresident for a year if they do not maintain a permanent place of abode in Maine, they maintain a permanent place of abode outside Maine for the entire year, and they spend no more than 30 days in Maine, counting any part of a day as a full day.
There is also a separate foreign safe harbor for certain people who spend at least 450 days in foreign countries during a 548 day period with limited days and no permanent abode in Maine. These rules are technical, so you should review Maine’s official guidance or work with a tax advisor if you think a safe harbor might apply to you.
Step 4: Maine-sourced income
Even after leaving Maine residency, you may still have tax obligations if you have income that originates from within the state.
Here’s how to handle Maine-sourced income after your move:
1) Ongoing tax responsibilities
If you continue to earn income from Maine, such as rental income, business profits, or wages, you will need to file non resident tax returns. These returns are structured so that only income sourced from Maine is taxed, while income earned outside Maine is handled under your new state and federal rules.
2) Rental or business income
Any rental properties or businesses you maintain in Maine will still be subject to the state’s tax laws. Make sure you understand the ongoing tax implications and keep clear records to help you stay compliant with Maine tax rules. Consulting with a tax advisor is highly recommended to navigate these complexities.





